Intune
How to Set Up Mobile Application Management for Android Devices with Intune
Topics: Intune
Following our exploration of Mobile Application Management (MAM) for Windows, this post covers how to configure MAM for Android devices. Learn how to enable secure Android access to organizational resources from unmanaged devices through app protection policies.
How does Mobile Application Management (MAM) work? MAM allows IT admins to implement rules on approved applications within Intune, focusing on app-level management without requiring device enrollment.
Who should use MAM? MAM serves users who need access to organizational resources—like emails and team meetings—on personal devices without enrolling in the company’s device management system.
Before diving into the specifics of creating a Conditional Access Policy, it’s important to understand how it enhances your organization’s security posture. This policy acts as a safeguard, ensuring that only devices adhering to your app protection guidelines can access company resources. Let’s walk through the steps to establish this critical layer of protection for your Android devices.
Now let’s dig in and learn what we need to do to set up MAM for unmanaged devices.
Device Requirements
- Android 4.4 and later
- Company Portal App Required (authentication mechanism)
- Licenses:
- Microsoft Intune License
- Entra ID P1 License
Create Conditional Access Policy
Navigate to Microsoft Intune > Endpoint security > Conditional access > + Create new policy
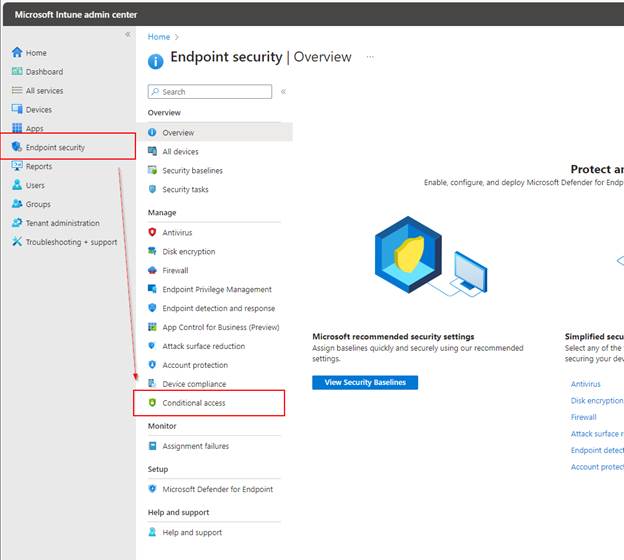
Create your Conditional Access Policy. Assign a descriptive name to the policy, such as “MAM for Android.”
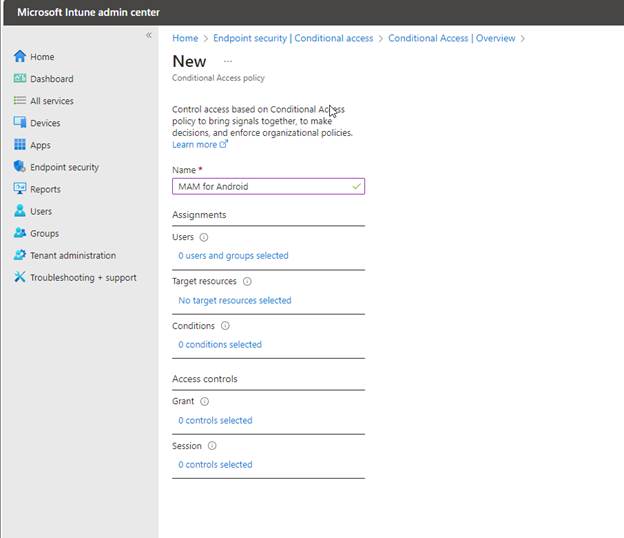
Assignments
Select the group the best fits your needs. In my case, I will choose “App Protection Pilot Group” which has a single user account that I will use to demo later.
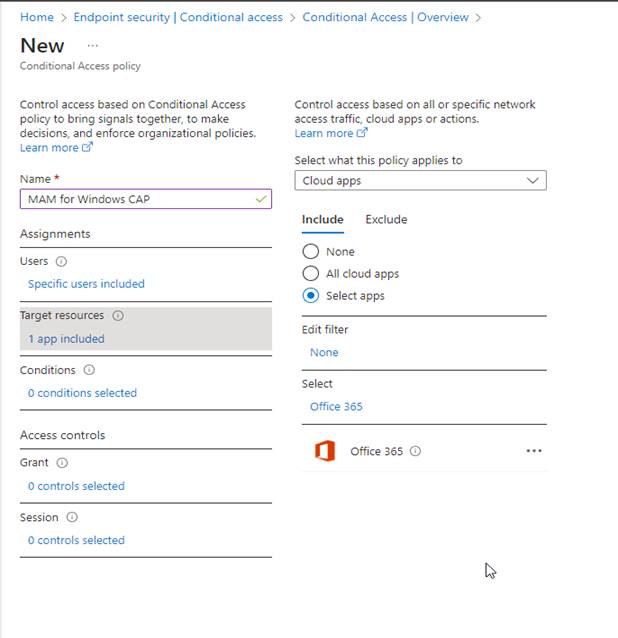
Targeted Resources
Choose the resources to protect, such as “Cloud Apps” or specifically “Office 365.” You can also select All cloud apps to broaden your scope, but for simplicity’s sake I will select Office 365.
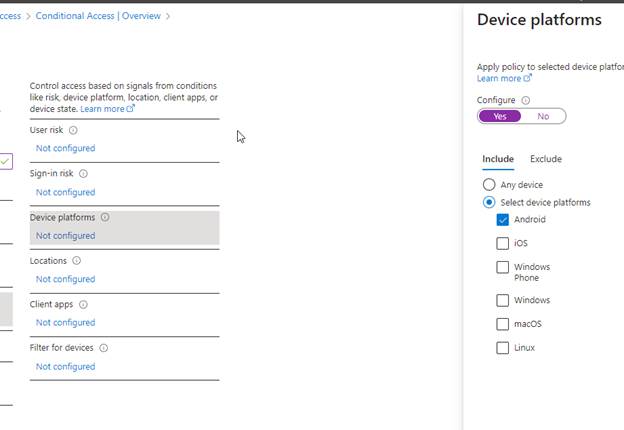
Conditions
Set the conditions targeting the Android Device Platform, as this will tell us the platform the user is signing in from.
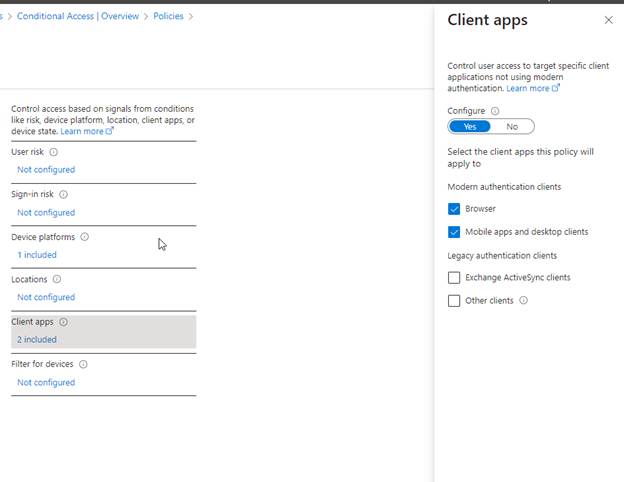
Under Client apps, select both Browser and Mobile apps and desktop clients.
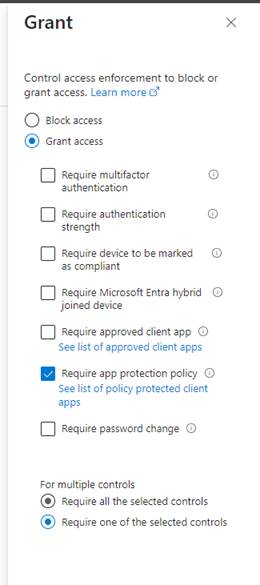
Access Controls
Next, go down to Access Controls and specify the requirements to get access. I’ve chosen Grant access by Requiring app protection policies to be in place.
Enable Policy
Activate the policy by setting the toggle to On, then click Save.
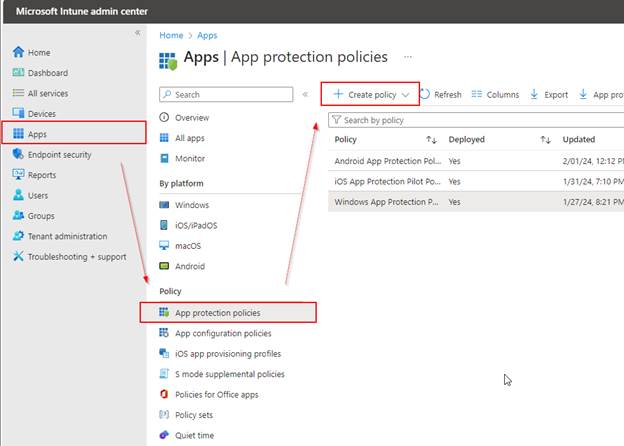
Create an App Protection Policy for Androids
Go to the Intune Admin Center > click on Apps > App protection policies > + Create policy > Android
MAM for Android Policy Configuration
On the create policy page give your policy a name and a description to help others understand your policy > click Next.
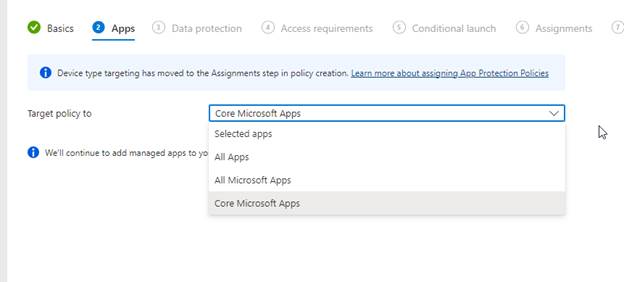
This is where Android gets a little more love. You can broaden your scope of targeting policies to a good number of applications. Your options are shown below. In my case, I will target All Microsoft Apps.
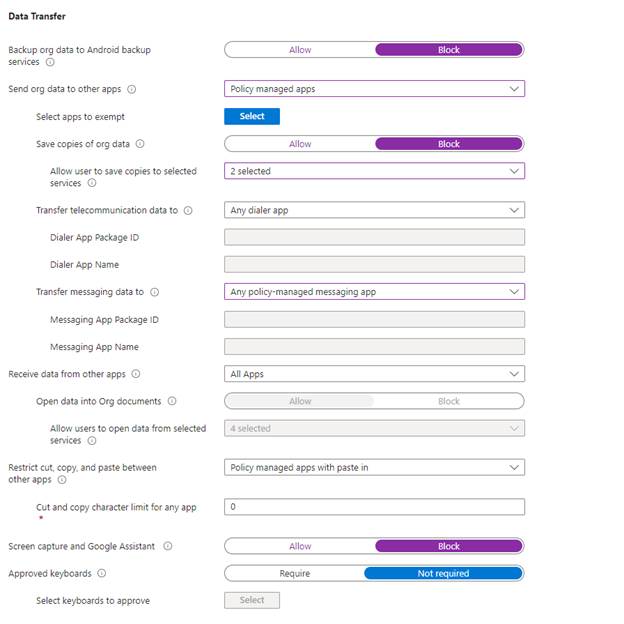
Data Transfer Restrictions
Next, create policies to control actions like cut, copy, paste, as well as other restrictions.
Below you can find all my policy choices. Here I will highlight a few and why I made these choices.
Backup org data to Android Backup Serices: Set to block to prevent data leaks. I want to avoid storing sensitive work or school data in an Android backup service.
Save copies of org data: Set to Block to disallow saving sensitive data on unmanaged resources. I do not want to allow users to save potential sensitive data on unmanaged resources, but I will allow users to save org data on managed services like SharePoint and OneDrive.
Restrict cut, copy, and paste between other apps: Allow only for managed apps, with paste-in enabled. This helps mitigate the risk of users copying sensitive information on unsupported platforms.
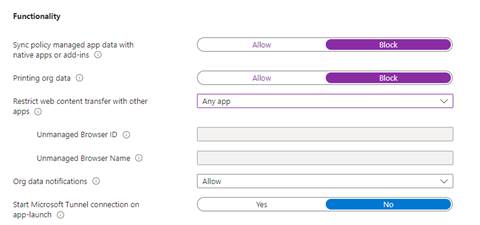
Encryption and Functionality
Now let’s require the encryption of org data on all devices accessing it on this app.

Next up, functionality. Here I went ahead and Blocked the Sync policy managed app data apps or add ins so that we are consistent with keeping org data contained and not intermixed. I also Blocked Printing org data to keep org data from leaving unmanaged platforms.
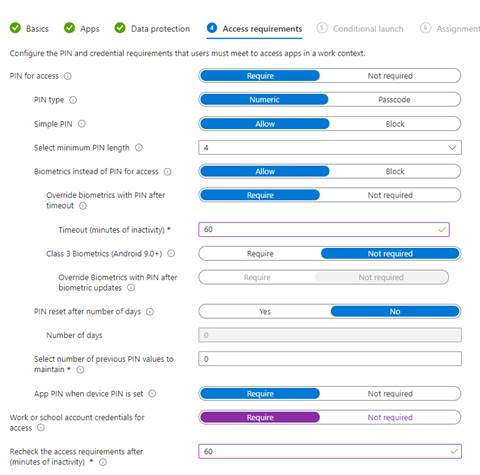
Access Requirements
Here we will set rules for users to access apps. I did keep the defaults, which require a PIN to access the apps. The PIN is set at the device level so if a user does not have a PIN enabled, they will not be able to access apps. I’m also requiring an app pin to access a resource such as Outlook for an extra layer of protection, along with requiring users to use work or school credentials for access. Once set, click next.
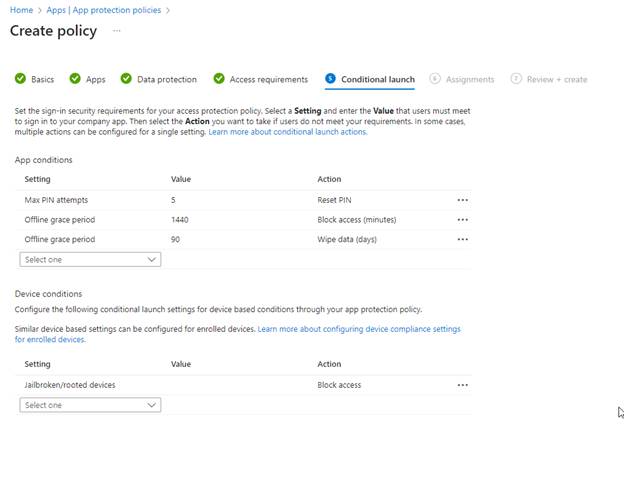
Conditional Launch
Here we set requirements for our App and Device conditions. We can also set actions. For example, if a device is detected as “Jailbroken” or “Rooted” it will Block access to the org’s application. I did not make any changes, keeping the defaults. Click Next.
Go ahead and select your Assignments. I chose the App Protection Pilot Group to keep things consistent.
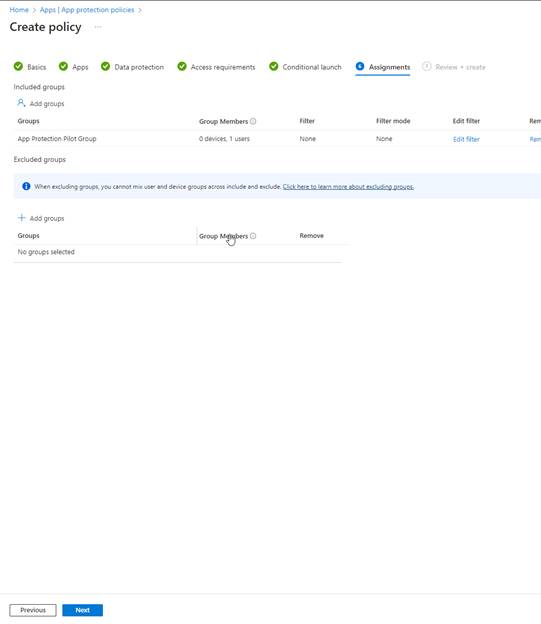
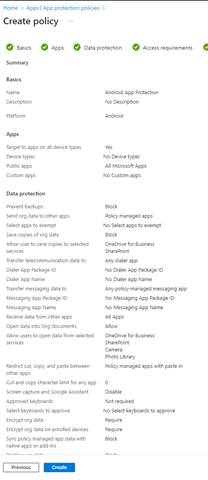
Review and then create your App Protection Policy once you have verified this meets your needs.
Time to Test MAM for Android
The work is done. Let’s test it out. I am going to access my unmanaged Android device with the company portal installed. I will first go to Google chrome and try to access Word.
As suspected, because I was not using an app with an App Protected policy, I was blocked and asked to Launch in Edge. Perfect.
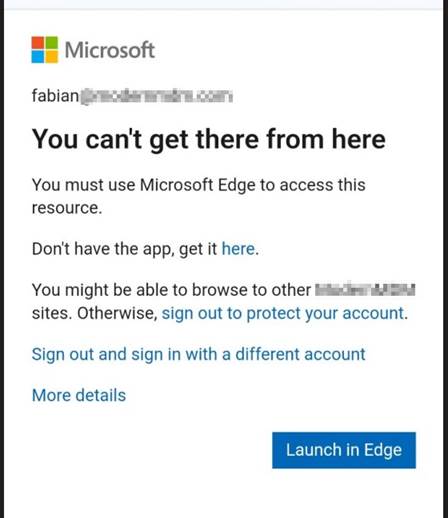
Funny enough, Edge did not like me either, because I first need to Sign in to Microsoft Edge to register my device.

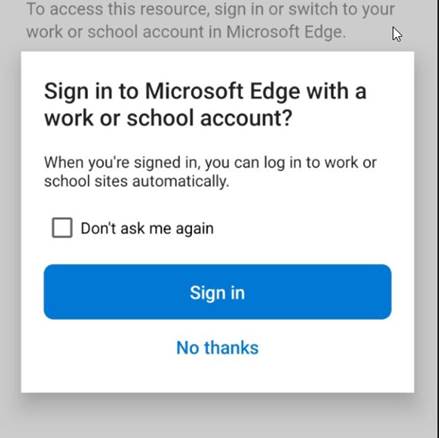
Now that I registered my phone, I head over to Microsoft Word and find the following message, which is a good indication.
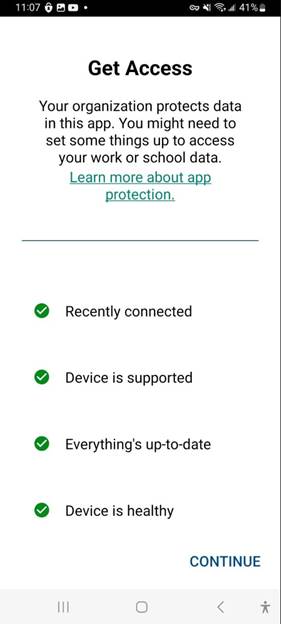
Great. Now we are inside the Word App with an app protection policy enabled.
Let’s test the copy and paste restriction policy on unmanaged apps. I am going to go into a .docx, try and copy text, and paste it to an unmanaged Samsung notes app on my BYOD device.
Now let us try to paste this text into an unmanaged app. Success org data is staying safe inside.
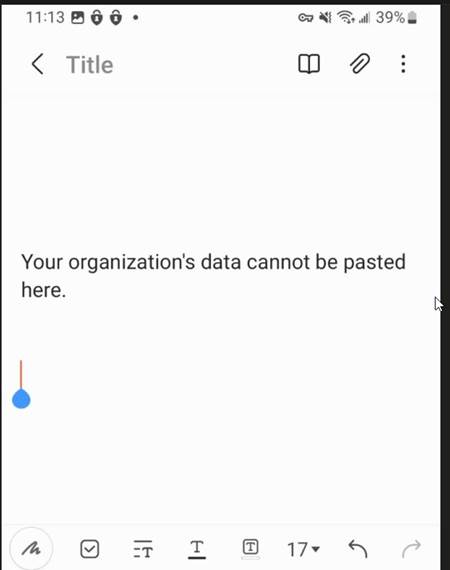
Conclusion: MAM for Android with Intune
Establishing Mobile Application Management (MAM) for Android devices through Intune is an important step towards securing organizational data while accommodating the flexibility needs of your workforce. By carefully creating Conditional Access and App Protection policies, you ensure that only compliant devices can access sensitive company resources, effectively mitigating potential security risks. This process enhances your organization’s security posture and supports a seamless user experience by allowing employees to safely access work data from their personal devices.
Remember, the correct setup of MAM is not just about enforcing security measures; it’s about enabling productivity and flexibility in a secure, controlled manner. Ensuring these policies are correctly implemented paves the way for a robust, agile IT environment that is both secure and user-friendly.