Application Management and Patching
Deploying Third-Party Applications with Intune Enterprise Application Management
Today, we’ll explore the third-party application management tool built into Microsoft Intune—Enterprise App Management (EAM), which is part of the Intune Suite. In this guide, I’ll show you how to deploy and update third-party applications using EAM.
Key Benefits of Using Enterprise App Management
Why use this tool? It simplifies the deployment of popular third-party applications such as Google Chrome and Zoom, boosting productivity and streamlining operations. It streamlines application management by enabling deployment and updates directly from the Intune console. It reduces the risk of unauthorized software and ensures applications remain current, which helps reduce security vulnerabilities.
From an IT pro’s perspective, not having to manage the lifecycle of third-party applications without complex configurations is a major time-saver. It allows you to focus on solving other business challenges instead of spending countless hours on packaging and updating applications.
How are these applications deployed, and are the necessary binaries pre-populated? They are deployed as Win32 apps that are prepped and hosted by Microsoft. Microsoft handles converting apps to Win32 and populating all the required information. The Enterprise App Catalog currently includes over 400 applications. If you need additional options or find that some applications are missing, consider Application Manager or Application Workspace, which offer a catalog of over 5,000+ apps.
What is the cost? You can purchase EAM as an add-on within the Intune Suite, and it is currently priced at $2 per license per month.
Requirements
Microsoft Intune Enterprise Application Management License
Step-by-Step Deployment Guide
First go to Microsoft Intune > Apps > Windows.
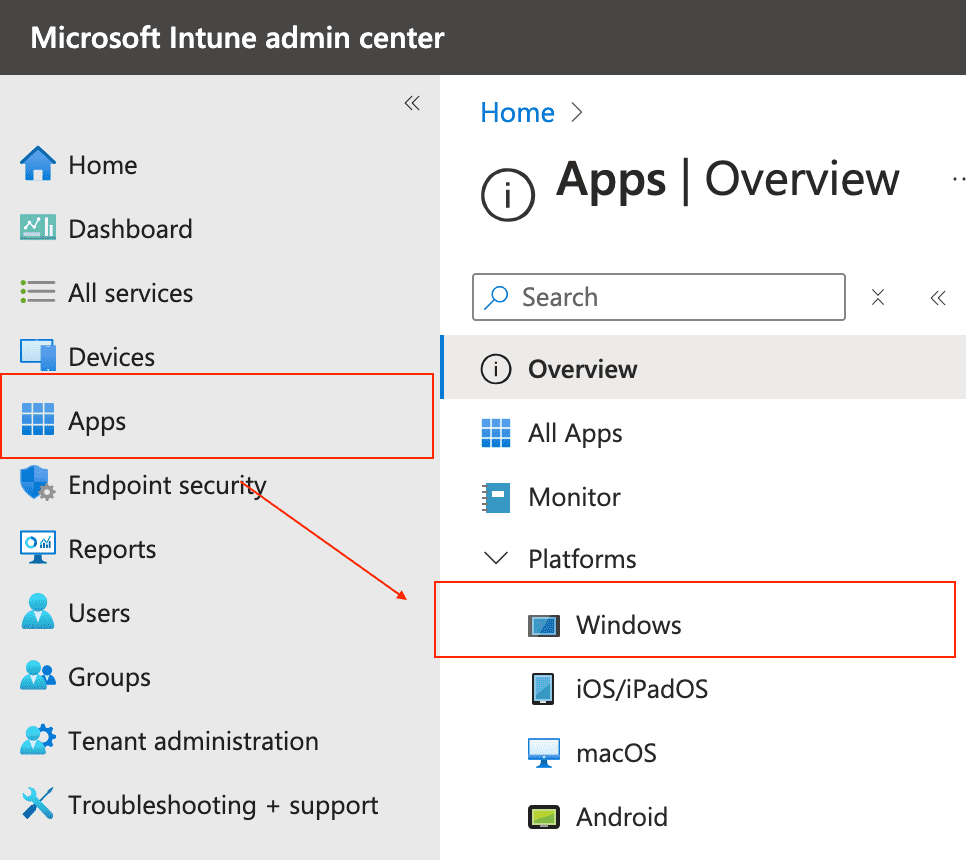
On the Windows app page, click +Create and choose Enterprise App Catalog app under Other.
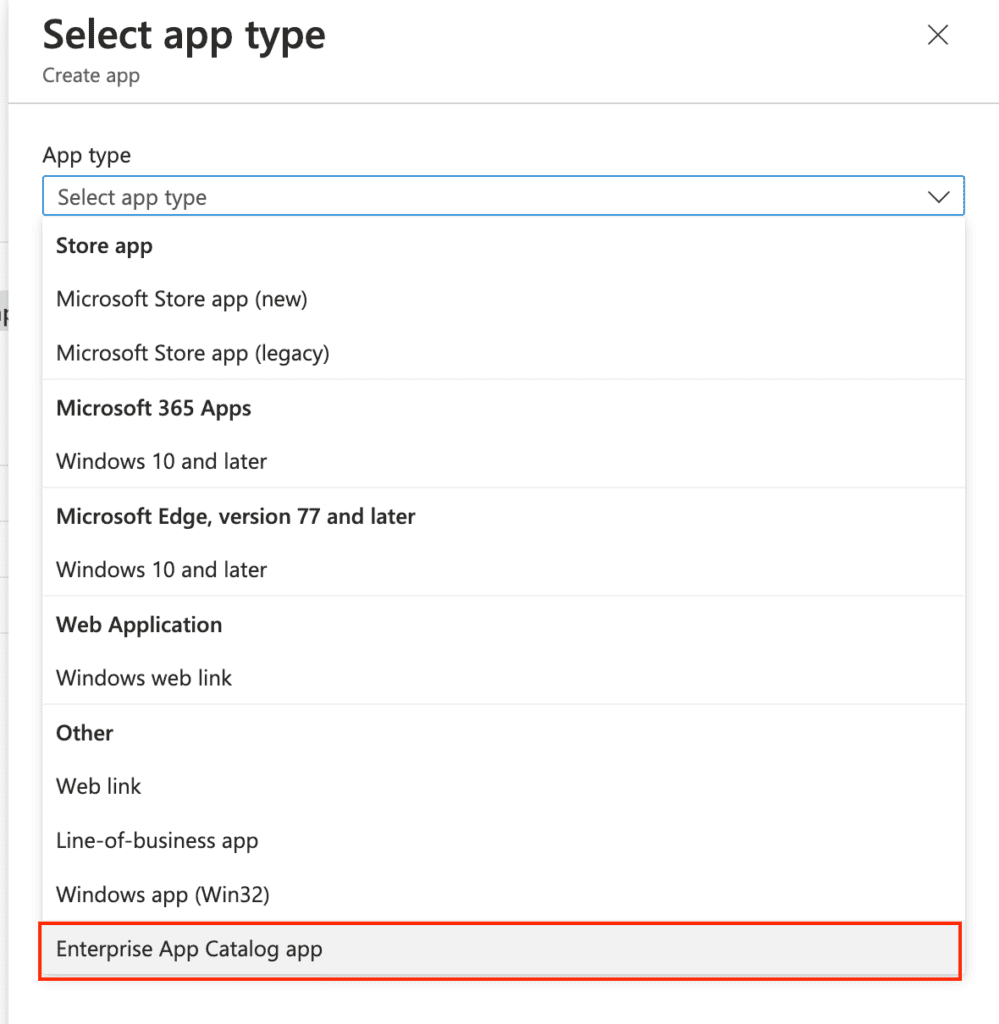
After selecting the Enterprise App Catalog app, you will be prompted with additional information and a link to learn more about these apps. Click Select to proceed.
On the next page, you’ll see the Enterprise App Catalog displaying apps by name and publisher. You can manually search for an application or browse using the scroll bar. Click on “Search the Enterprise App Catalog located to the right of Select app to view the catalog.
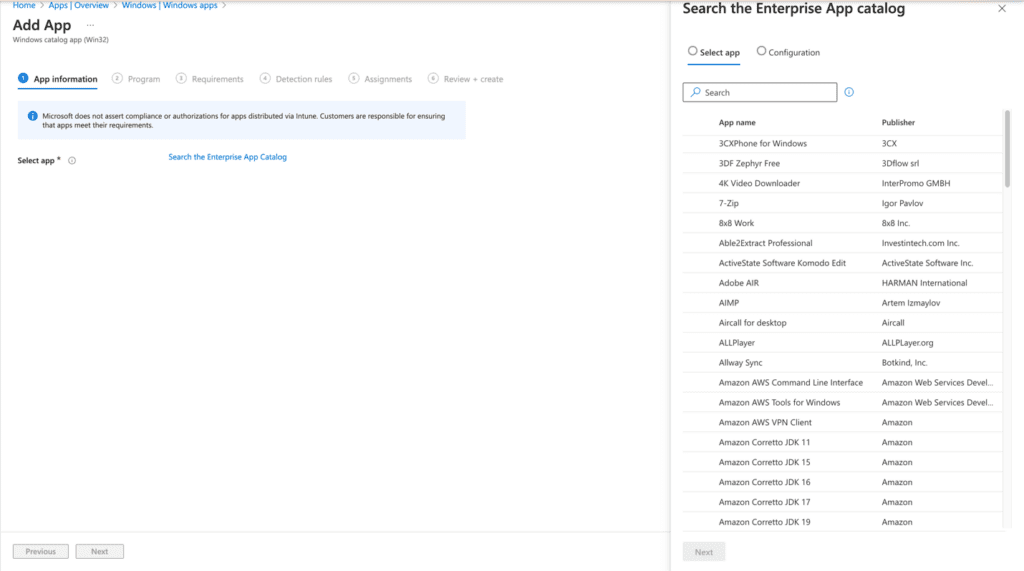
In this guide, I’ll focus on deploying two applications: Google Chrome for Business and Jabra Direct. I chose these because they handle updates differently. Google Chrome for Business updates automatically, with updates delivered directly from the publisher. In contrast, Jabra Direct must be updated via the Monitor report in Intune, requiring the creation of a new app with a supersedence relationship since it does not update automatically.
Configuring Google Chrome for Business
To start, I searched for Google Chrome for Business using the search bar > click Next.
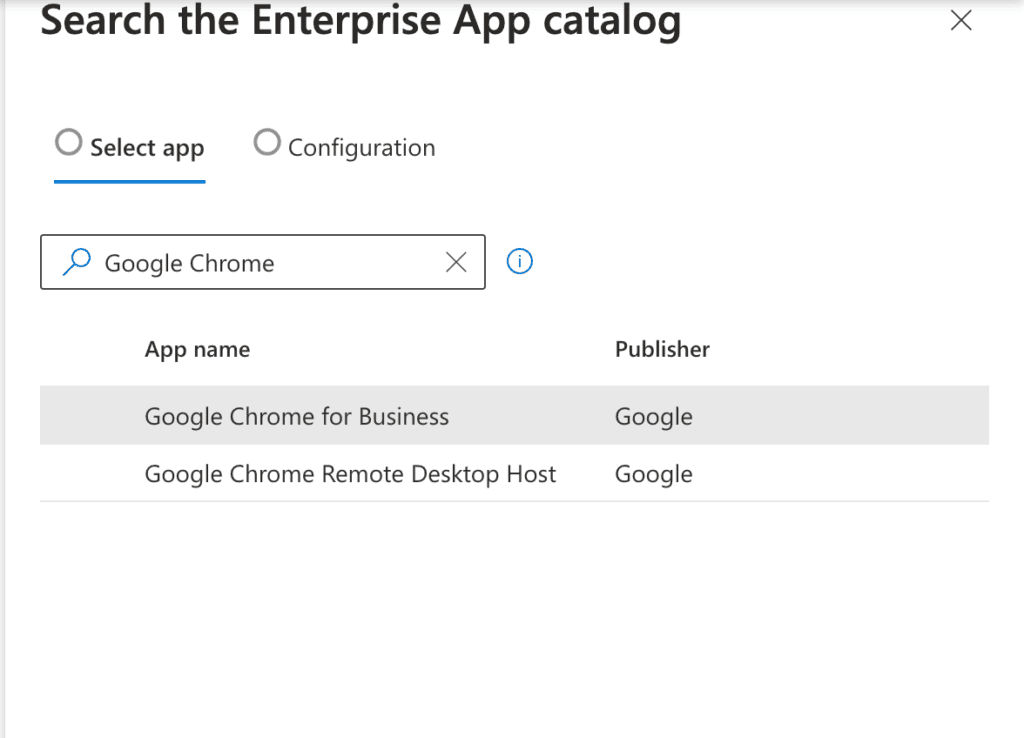
After selecting Google Chrome for Business, the Configuration pane appears, displaying details about the app. For example, you can see that the app auto-updates with publisher-delivered updates. Additionally, details such as language, architecture, and version are shown. Click the Package name and then Select to proceed.
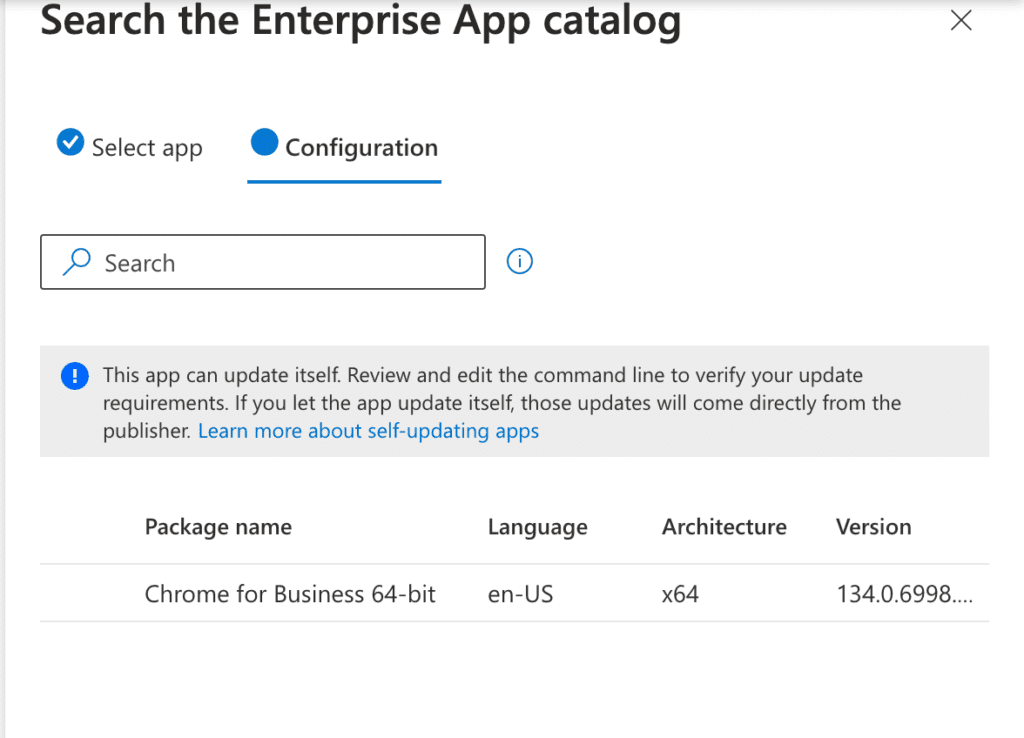
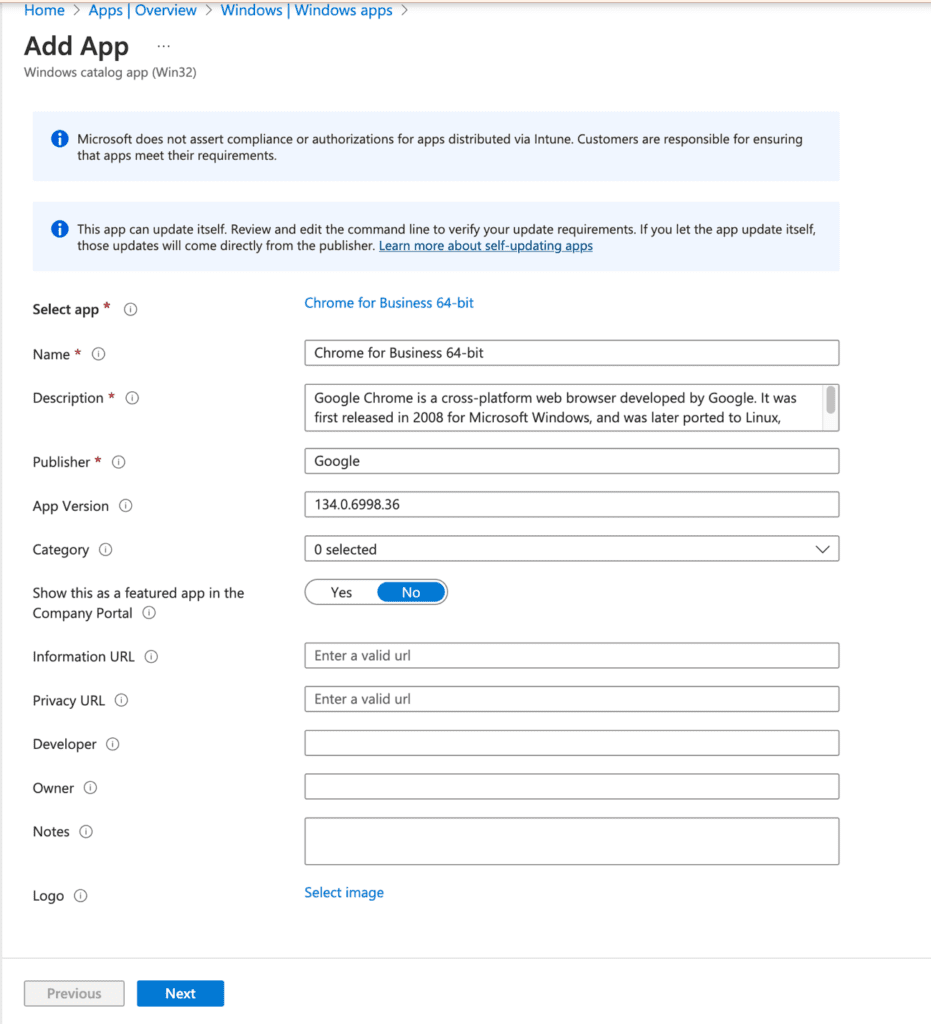
As noted, the app information is prefilled. You can make changes if needed, but for this demonstration, I’ll use the default settings. Click Next.
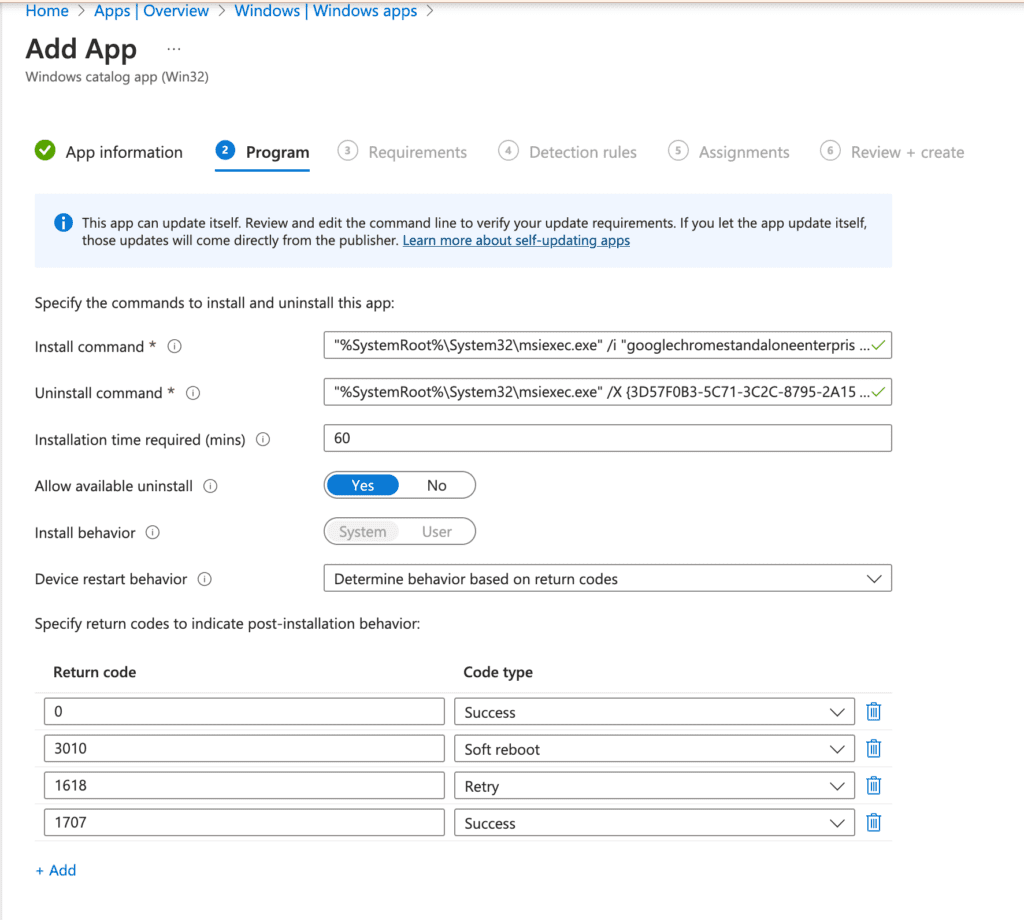
Next, you’ll reach the Program section. One highlight is that the binaries are already provided, saving you the time of searching for this information. The section displays details on install and uninstall commands, as well as device restart behavior. Click Next to continue.
On the Requirements page, the necessary information—such as operating system architecture and minimum operating system—is pre-selected. Click Next.
The Detection Rules page displays pre-configured rules, saving you setup time.
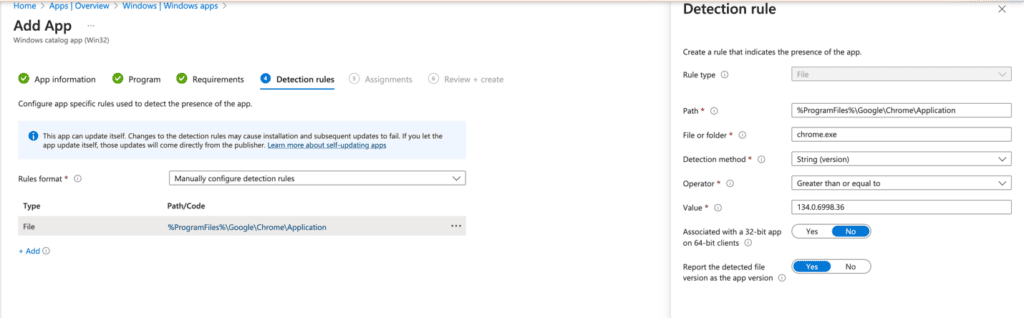
Now that you’ve reviewed the prefilled information in the Enterprise App Catalog, let’s deploy the app to an end user’s device. Select this application as “Required” for all users so that Google Chrome for Business is automatically available without user intervention. It is recommended to begin with a pilot group. Finally, click Review and Create.
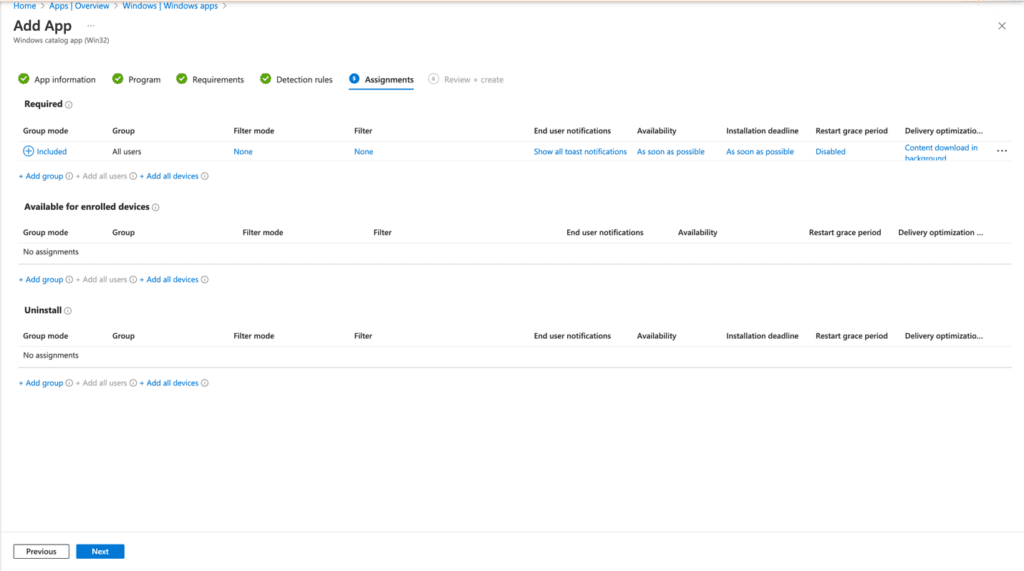
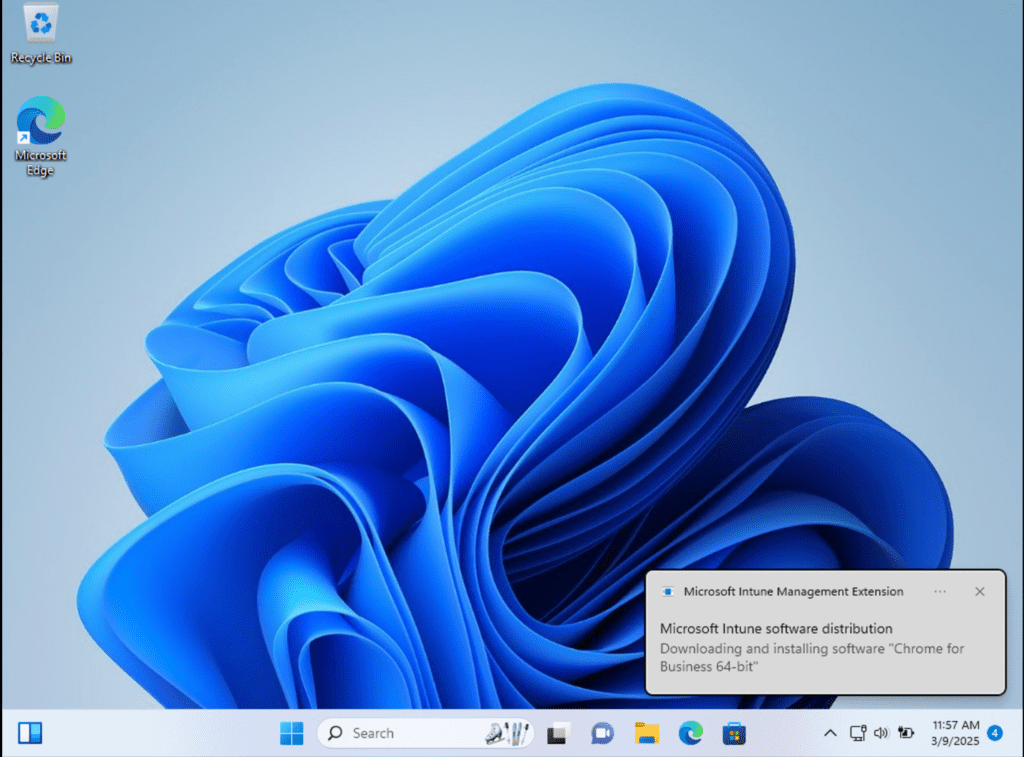
Let’s go check out the end user experience.
The end user receives a notification about the installation, and Google Chrome appears in the list of installed apps and programs.
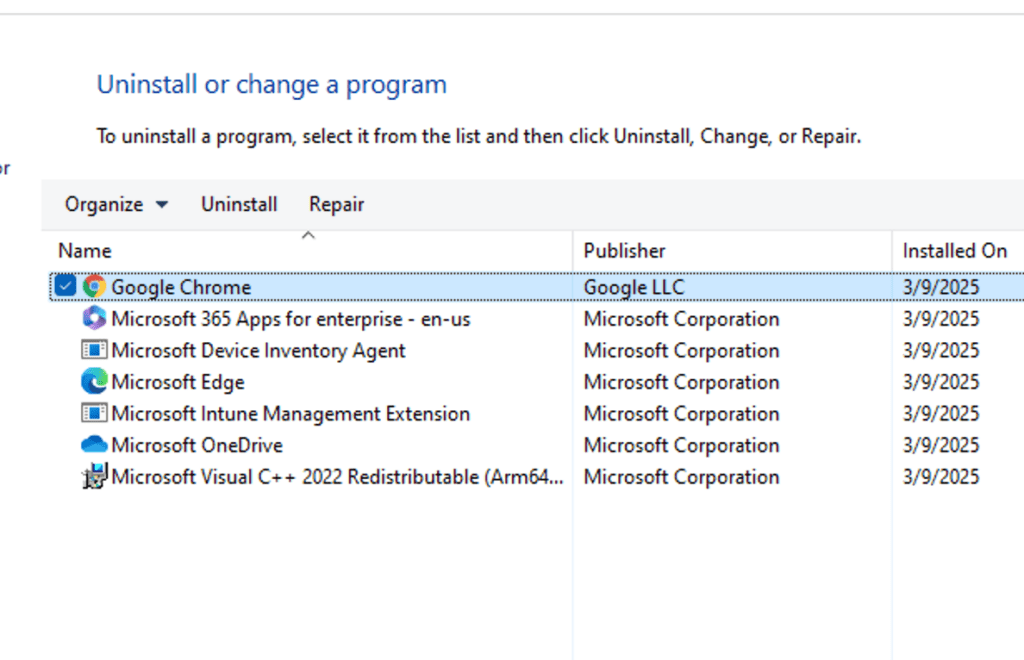
Deploying Jabra Direct and Managing Updates
Next, I’ll demonstrate the end-user and IT admin experience when an application cannot update automatically. For this example, we’ll use Jabra Direct.
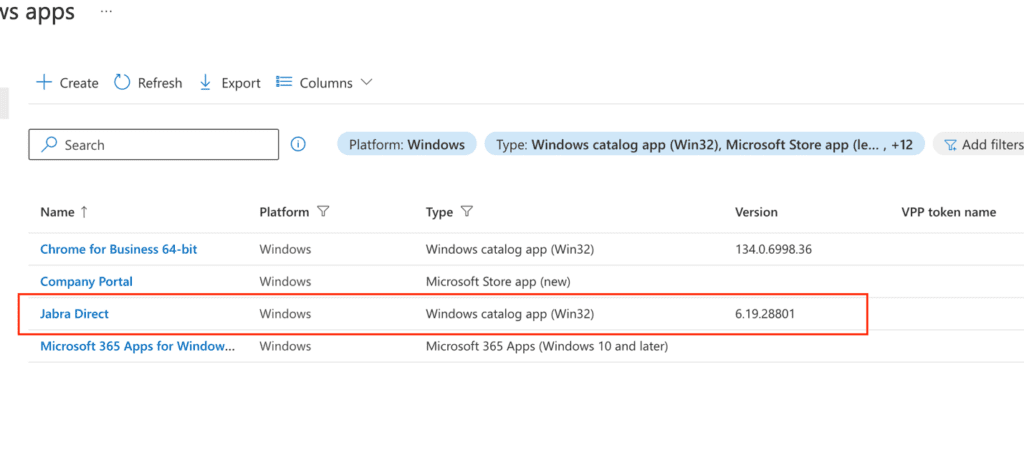
Next, navigate to Microsoft Intune > Apps > Windows Apps and follow the same process until you reach the Enterprise App Catalog. This time, search for Jabra Direct and complete the creation steps. Once complete, the app appears as a Windows catalog app (Win32) with version 6.19.28801 in Intune. (Note: Versions may vary; this example simplifies the update from version 1.0 to 2.0.)
End-User Experience: After deploying the Jabra Direct app, verify its installation and version number locally by navigating to Settings > Apps > Apps & features.

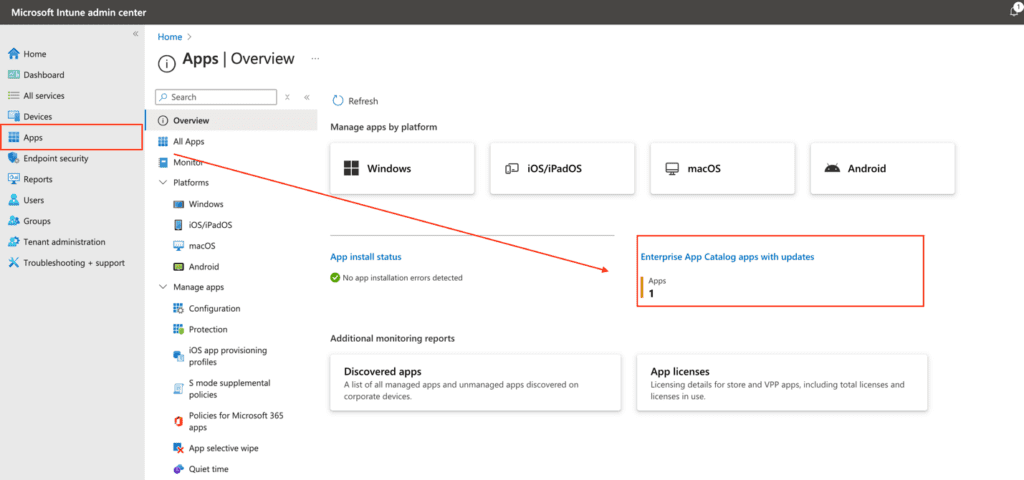
Applications often receive new security and feature updates. For apps that cannot update automatically, you must create a new app with a supersedence relationship. To do this, navigate to Microsoft Intune > Apps > Overview, then select Enterprise App Catalog apps with updates. You can also click on “Monitor” to access this section.
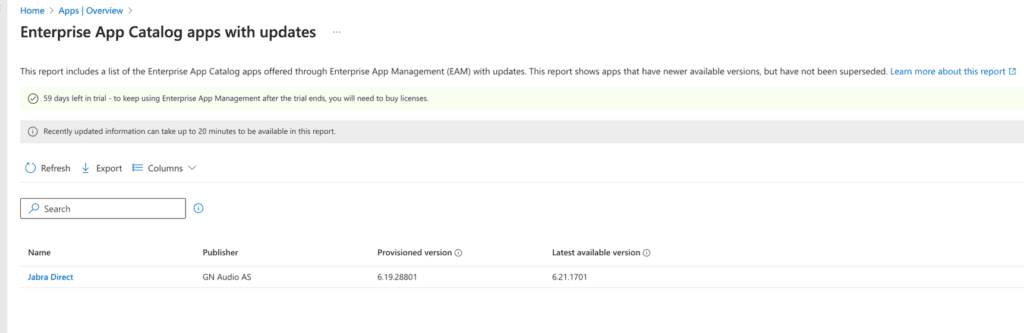
On that page, you will see applications requiring updates. In this example, Jabra Direct version (6.19.28801) has a newer version available: Jabra Direct (6.21.1701).
To update the app and supersede the old version, click on Jabra Direct. On the app page, the newer version is displayed in the Enterprise App Catalog. Click Update to initiate the update process.
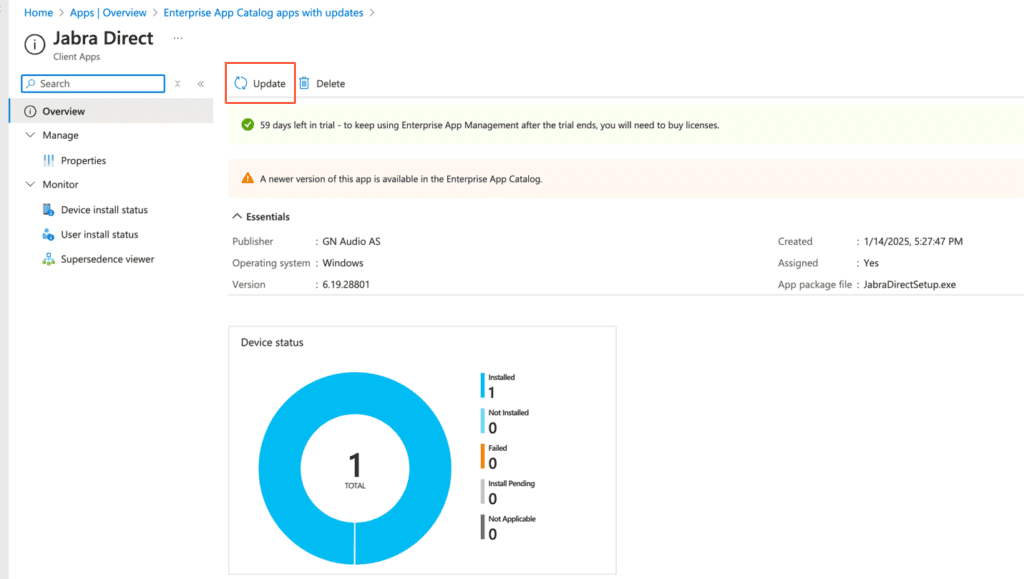
After clicking “Update,” a prompt appears, informing you that a new application will be created with the updated version and a supersedence relationship will be established. The prompt also notes that certain settings, such as scope tags and assignments, will not be copied over. Click Supersede app to proceed.
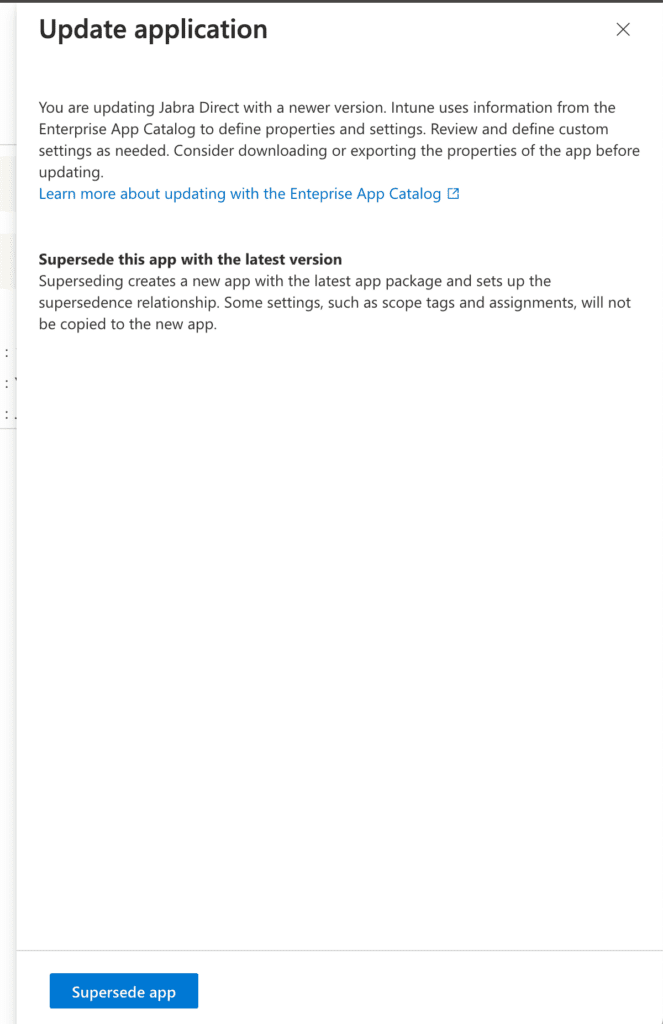
The process is similar to the initial application creation, but this time with the new version (6.21.1701). Proceed through the steps until you reach the Supersedence section. (For this demonstration, you can skip to step 5, as most settings remain unchanged except for some detection rule modifications.)
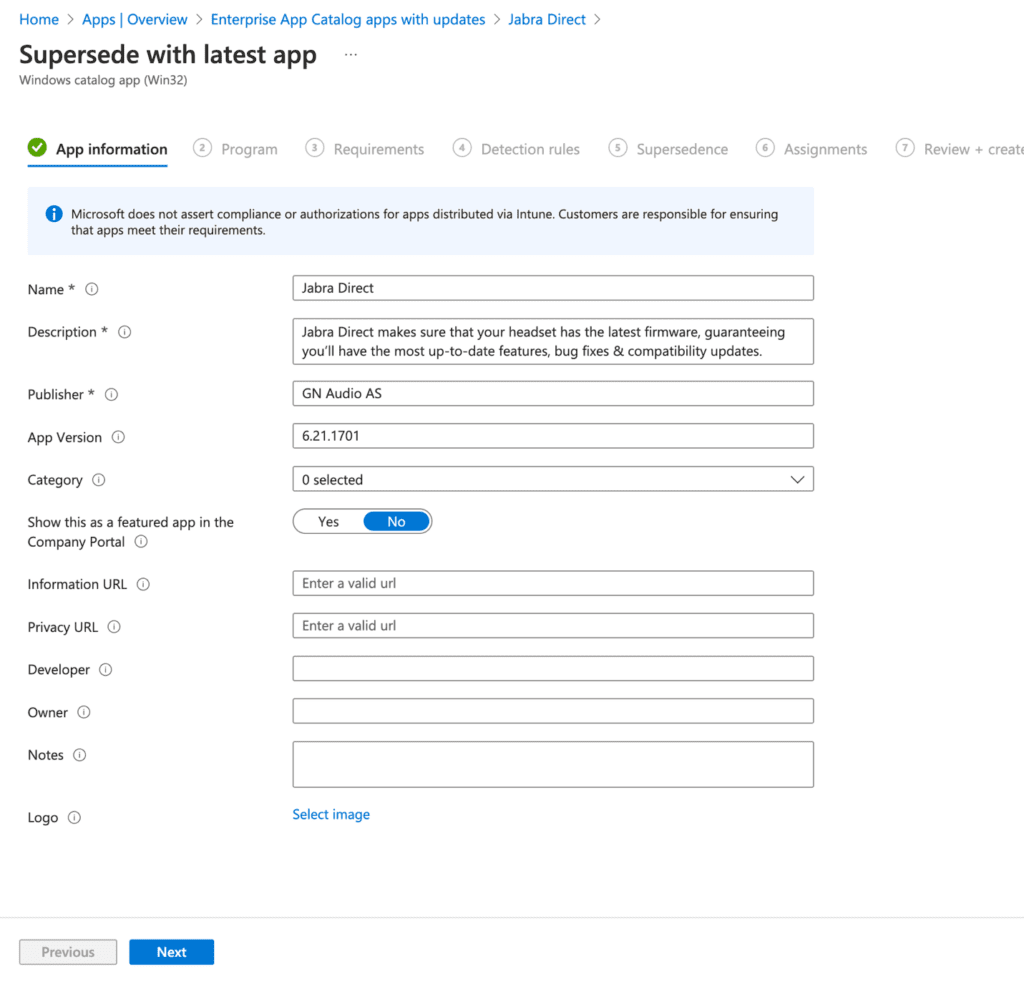
In the Supersedence section, you’ll see the old version of Jabra Direct. Choose whether to uninstall the previous version or retain it. For this demo, select Yes to uninstall the previous version.
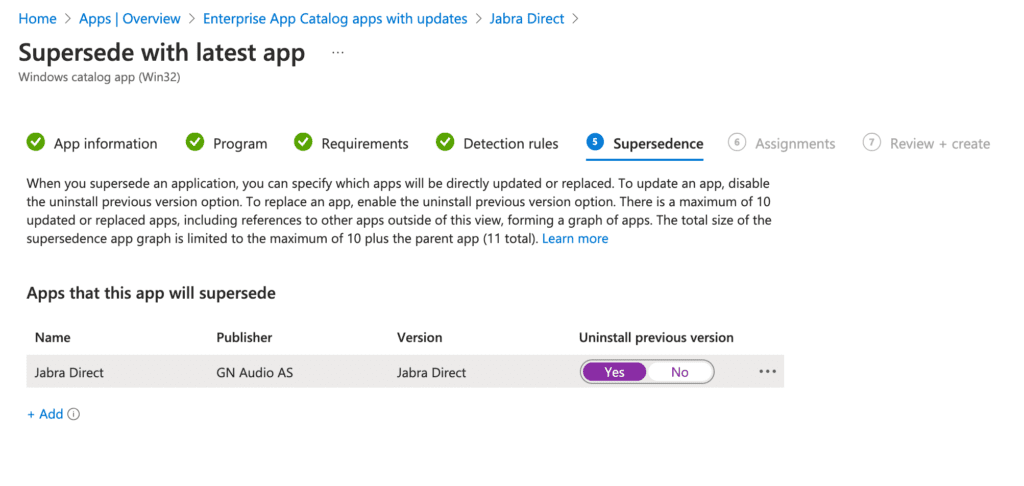
Note that the update process may not carry over certain assignments from the original Jabra Direct application, so you may need to reconfigure them. In this example, I’ll deploy the updated application as Required for all users, ensuring the old version is uninstalled and replaced.
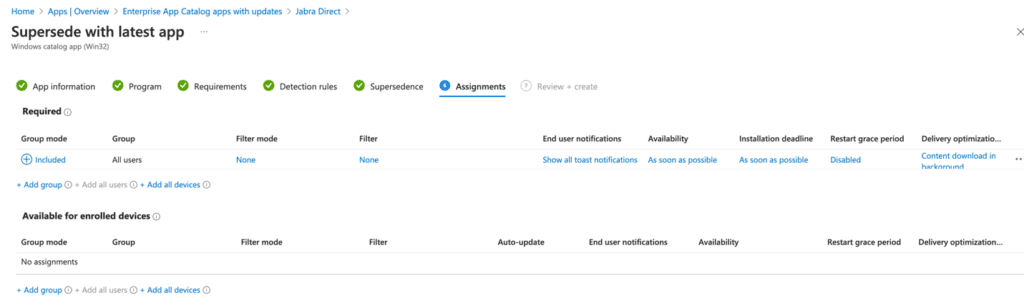
Review and create.
Finally, review the end-user experience during the update process, which uninstalls the old version.
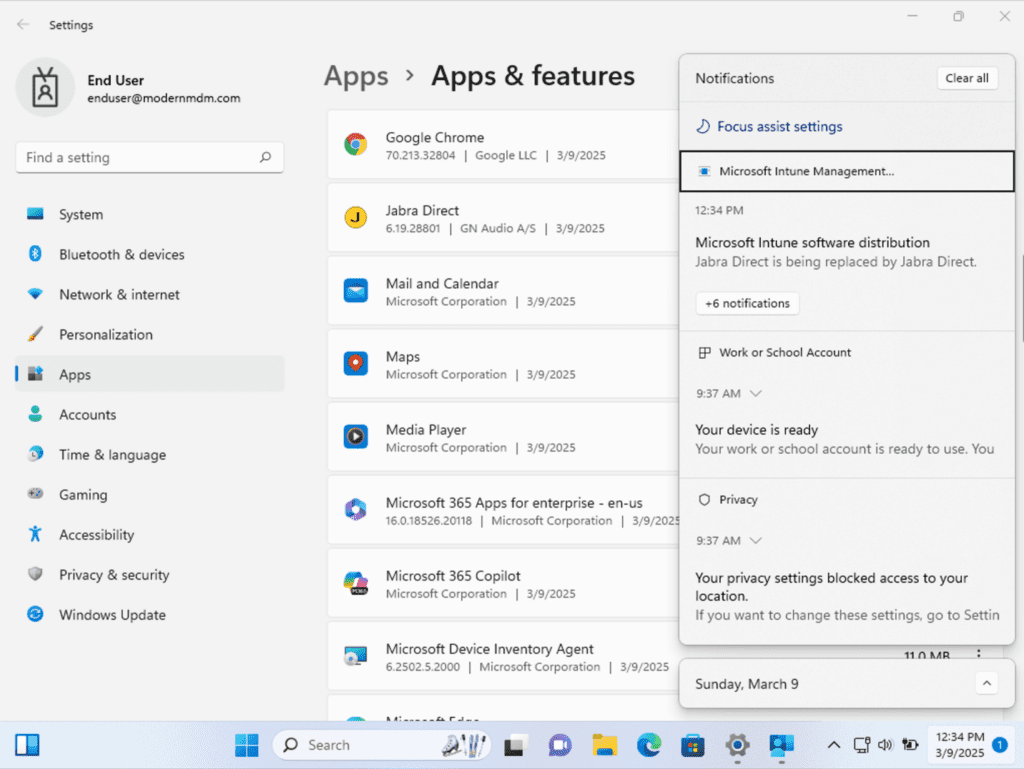
Before update:

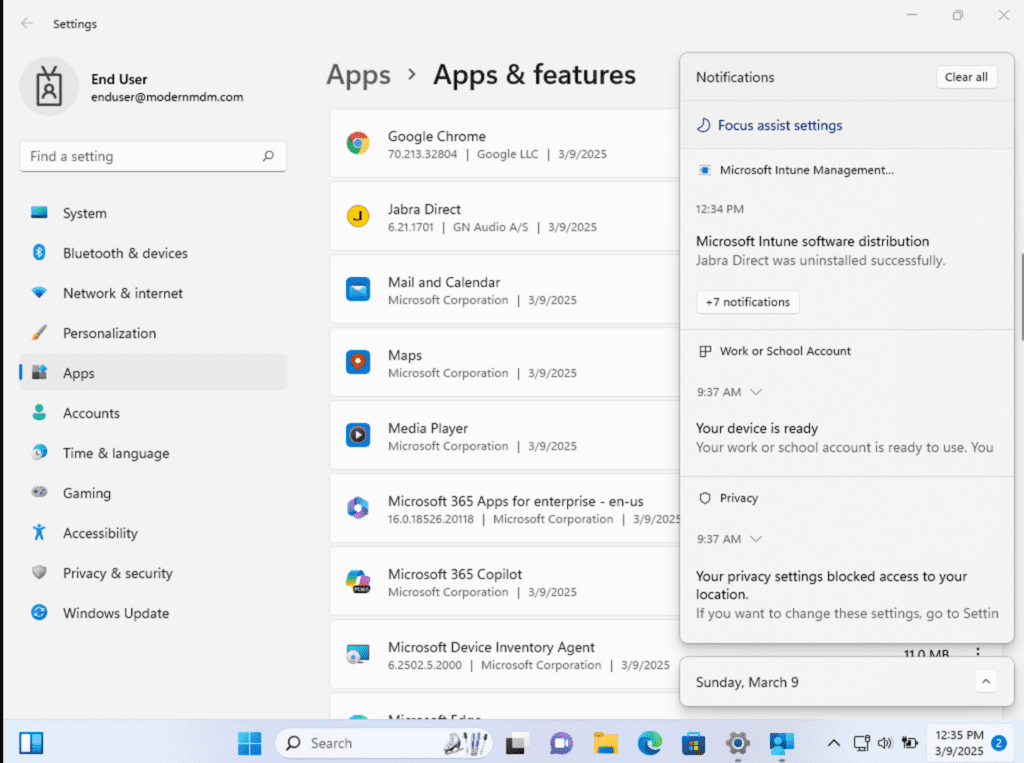
During the update, you will receive a toast notification indicating that Jabra Direct is being replaced, the old version has been uninstalled, and the new version (6.21.1701) has been successfully installed, as shown in the third screenshot.
Conclusion: Third-Party Applications Deployed with Intune Enterprise Application Management
Thank you for following along. Enterprise App Management is a solid native tool within Microsoft Intune, offering a decent catalog selection. However, it does have limitations, such as the inability to fully automate the lifecycle of third-party applications and limited customization options. If these features are critical for your organization, consider exploring Recast Software’s Application Manager or Application Workspace. We hope this guide helps you streamline third-party app patching.