Intune
Client Management with Microsoft Defender and Microsoft Intune: A Comparative Guide for Security Profiles
Topics: Intune, Systems Management
Managing and securing client devices is key to smooth IT operations. Organizations need reliable tools to set up security profiles, keep track of compliance, and deliver a smooth experience for users. Microsoft offers two tools to help with this: Microsoft Defender for Endpoint’s Client Management and Microsoft Intune. Both tools aim to boost endpoint security, but they have different focuses and unique features. Let’s dive into the specifics to understand their differences and use cases.
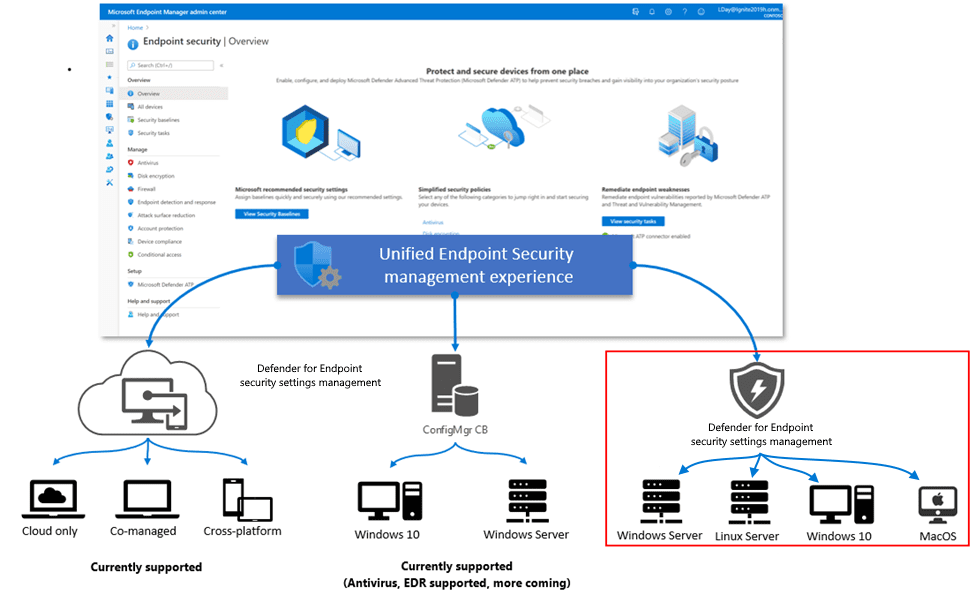
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Client Management: Focused Endpoint Security
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (MDE) is Microsoft’s enterprise-grade endpoint detection and response (EDR) solution. Its client management features let organizations easily deploy and manage security profiles right on their devices. Here’s what makes Defender Client Management stand out:
Key Features
- Native Security Profile Management: Deploy security settings—including antivirus, firewall rules, and attack surface reduction (ASR) policies—directly from the Defender portal.
- Simplified Onboarding: When you enroll devices in Defender, they’re automatically set up for client management, making deployment easier.
- Advanced Threat Protection: Integrated threat detection and response features allow IT admins to monitor and respond to security incidents in real-time.
- Scalable to Multi-platform Environments: Supports Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS devices.
Use Cases
- Quick Security Setup: Great for organizations that want to set up basic security policies without the extra burden of a full MDM (Mobile Device Management) solution.
- Small IT Teams: Provides an easy-to-use interface for managing security without requiring deep technical expertise.
- Integrated Threat Response: Perfect for companies already leveraging MDE’s threat detection and response capabilities.
Limitations
- Narrower Focus: Designed primarily for security settings, offering limited device management features.
- Dependent on Defender for Endpoint Licenses: Requires appropriate MDE licensing, which might not cover all endpoint management needs.
Microsoft Intune: Comprehensive Endpoint Management
Microsoft Intune, part of the Microsoft Endpoint Manager suite, is a flexible MDM and Mobile Application Management (MAM) solution. It provides complete client management—from setting up security profiles to handling other device management tasks.
Key Features
- Comprehensive Policy Management: Enforce security baselines, compliance policies, configuration profiles, and conditional access.
- App and OS Management: Beyond security, Intune supports application deployment, OS updates, and detailed configuration of device settings.
- Granular Control: Offers detailed customization for a wide range of scenarios, including BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) and COPE (Corporate-Owned, Personally Enabled).
- Zero Trust Integration: Integrates with Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) and Conditional Access policies to enforce Zero Trust principles.
- Flexible Enrollment Options: Supports automatic enrollment via Azure AD join, Group Policy, and other methods.
Use Cases
- Enterprise-grade Device Management: Great for large organizations with a variety of device types and setups.
- Compliance-Driven Environments: Essential for industries with strict regulatory requirements.
- Unified Management: Ideal for organizations looking to consolidate application, device, and security management in a single solution.
Limitations
- Complexity: A steep learning curve for organizations new to endpoint management.
Comparing Security Profiles: Defender vs. Intune
Policy Scope
| Feature | Microsoft Defender Client Management | Microsoft Intune |
| Antivirus Configuration | Yes | Yes |
| Firewall Management | Yes | Yes |
| ASR Rules | Yes | Yes |
| Compliance Policies | No | Yes |
| Conditional Access | No | Yes |
| App Management | No | Yes |
Scalability and Flexibility
| Attribute | Microsoft Defender Client Management | Microsoft Intune |
| Multi-platform Support | All common | All common |
| BYOD Support | Limited | Comprehensive |
| Advanced Customization | No | Yes |
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Needs
When deciding between Microsoft Defender Client Management and Microsoft Intune, consider your organization’s priorities:
Choose Defender Client Management if:
- You primarily need to enforce basic security settings.
- You run a small IT team or have minimal device management needs.
- You’re already using Microsoft Defender for Endpoint’s EDR features.
Choose Microsoft Intune if:
- You need a more complete solution for managing devices and applications.
- You operate in a compliance-driven or heavily regulated environment.
- You need advanced customization and policy control.
Conclusion
Microsoft Defender Client Management and Microsoft Intune are powerful tools tailored for different use cases. While Defender offers a straightforward approach to endpoint security, Intune provides a more comprehensive device management solution. Many organizations can benefit from using both tools together, employing Defender for advanced threat protection and Intune for broader device management. Understanding their features and limits can help IT admins make smart choices to boost their endpoint security and management strategies.
Recast Software has recently launched the Right Click Tools Browser Extension, bringing right-click actions to Intune and beyond. Speed up routine tasks, unify device management, and enhance security—all from your Intune console. Learn more here.